skip to main |
skip to sidebar



 Engine Trends:
Engine Trends:
The infernal combustion engine has been with us for a long time - since about 1885. Familiar layouts soon appeared with, for example, six cylinders seen as early as 1902. Multiple valves per cylinder, double overhead cam-shafts, super-chargers, turbo-chargers, and fuel injection are all well and truly pre-war. After that, it might be said that there was no very novel and lasting engine concept (perhaps the Wankel rotary engine excepted) until the oil crisis and stricter anti-pollution laws started a movement towards greater engine efficiency. Engines have grown more efficient and less polluting (if well maintained) since the 1980s but cars and 4WDs grew heavier and bigger in the 1990s as oil prices fell, cancelling out some of the gains. Some day oil will become inordinately expensive to use as a fuel, as OPEC's production squeeze of 2000 reminds us. Getting ready for that day, a number of refinements of, and alternatives to, the internal combustion engine are coming to show-rooms or running in laboratories and in test vehicles.
 WORKING OF A PETROL ENGINE The working of an internal combustion engine is divided into four stages called four strokes of the engine and hence the engine is called a four stroke engine.
WORKING OF A PETROL ENGINE The working of an internal combustion engine is divided into four stages called four strokes of the engine and hence the engine is called a four stroke engine.
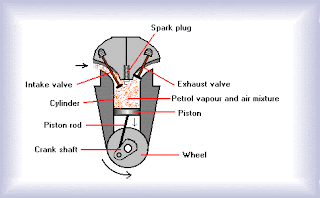
The intake stroke : When the engine starts, the piston moves downwards in the cylinder, because of which a region of low pressure is created in the cylinder, above the piston. At this moment, the intake valve opens and the fuel mixture(petrol vapour and air mixture) is sucked into the cylinder from the carburettor.
WORKING OF A PETROL ENGINE
The working of an internal combustion engine is divided into four stages called four strokes of the engine and hence the engine is called a four stroke engine.
The intake stroke :
When the engine starts, the piston moves downwards in the cylinder, because of which a region of low pressure is created in the cylinder, above the piston. At this moment, the intake valve opens and the fuel mixture(petrol vapour and air mixture) is sucked into the cylinder from the carburettor.
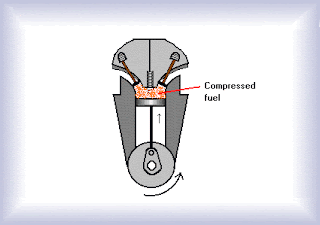
The compression stroke :
When the sufficient amount of the fuel mixture (petrol vapour and air mixture) has entered the cylinder, the intake valve gets closed. The piston is then forced to move upwards which compresses the fuel-mixture to about one-eighth of its original volume. Higher the compression ratio, more will be the efficiency of the engine.
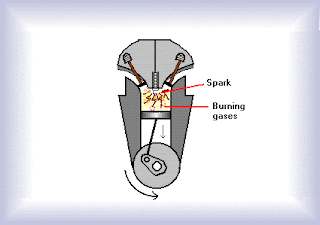
The power stroke :
Before the piston completes its upward movement, compressing the petrol vapour and air mixture, the spark plug produces a little electric spark inside the cylinder and this spark sets fire to the petrol-air mixture. The petrol vapour burns quickly in a little explosion, producing a large volume of gases and enormous heat. The heat thus produced expands the gases rapidly. The pressure of rapidly expanding hot gases pushes the piston downward with a great force. The piston pushes the piston rod and the piston rod pushes the crank shaft. The crank shaft is joined to the wheels of a car. When the crank shaft turns, the wheels rotate and move the car.
The exhaust stroke:
When the piston has been pushed to the bottom of the cylinder by the hot expanding gases in the power stroke, then the exhaust valve opens. After that, due to the momentum gained by the wheels, the piston is pushed upwards. The upward movement of the piston, expels the spent gases through the exhaust valve into the atmosphere, carrying away the unused heat. The exhaust valve then closes, the intake valve opens up, and the above four strokes of the engine are repeated again and again.
Classification based on : Cycles Compression Cooling Valve arrangement Cylinder arrangement Air and Fuel
There are two main types of petrol engines, reciprocating engines and rotary engines. Reciprocating engines have pistons that move up and down or back and forth. A part called a crankshaft changes this reciprocating motion into rotary motion. A rotary engine, also known as a Wankel engine, uses devices called rotors instead of pistons. The rotors produce rotary motion directly. This article discusses reciprocating engines, the more common type.
Reciprocating petrol engines are classified in a number of ways. These include :
(1) number of piston strokes per cycle,
(2) type of compression,
(3) by the way they are cooled,
(4) valve arrangement,
(5) cylinder arrangement, and
(6) way they are supplied with air and fuel.
 Inventor of Diesel Engine
Inventor of Diesel Engine
Rudolf Diesel was born in the year1858 in Paris. His love for his work could be seen from the fact that an explosion of an engine almost took his life but did not deter him from his work. His engine was the first that provided evidence that fuel could be ignited without a spark.
Types of Diesel Engine Diesel engines can be broadly distinguished as two-stroke and four-stroke. Bulky engines usually operate on the two-stroke cycle. Lighter engines generally operate on four-stroke cycle.
Generally cylinders are used in multiples of 2, 4, 6, or 8, .It doesn’t matter what number of cylinders are being used as long as the load on the crankshaft is counterbalanced to prevent excessive vibration. The inline-6 cylinder is used widely in medium and heavy duty engines.
Working of diesel engine. The temperature of gas rises when it is compressed. When the inlet valve opens air is sucked into the cylinder of a diesel engine due to vacuum created. The piston then moves upward and compresses air raising its pressure and temperature. As the piston moves up towards the end of compression stroke, injection of diesel fuel the combustion chamber that is cylinder takes place. There is high pressure inside cylinder so the fuel is injected through an atomizing nozzle at reasonably high pressure. The mixture of fuel and air then ignites and burns rapidly. The gas in the chamber expands. This forces the piston to move down and thereby producing power stroke. The connecting rod which is linked to crankshaft forces it to turn and delivers rotary power at the output end of the crankshaft. Scavenging of the engine is completed either by ports or valves.Accessories of diesel engine
Turbocharger is a vital accessory and is used to compress the intake air. To increase the efficiency an after cooler/intercooler is used to cool the air after compression. Speed of the engine can be controlled using Governor by adjusting the rate of fuel delivery. In cold weather conditions these engines can prove problematic. To overcome this problem small electric heater called glow plug is used inside the cylinder to warm the cylinders prior to starting. While you can also have resistive grid heaters in the intake manifold to warm the inlet air until the engine reaches operating temperature. Engine heaters fixed into the utility grid are mostly used when an engine is shutdown for long period in cold weather to lessen the startup time and engine wear.Comparison with gasoline engine :
Diesel engine is more efficient than gasoline engine as they have comparatively high compression ratio. Gasoline engine limitation is that it cannot be used for heavy duty applications as the components cannot withstand the stress caused on them. Diesel engines have longer life.
For the same power produced diesel engines are heavier compared to petrol engine.
Diesel engine causes more pollution as compared to gasoline engines which are eco friendly. When compared on cost basis diesel engines prove to more expensive. Also diesel fuel is not easily available as gasoline. The noise and vibration produced by diesel engine makes them less popular.Applications: The diesel engines used today are more superior to Rudolf Diesel's original concept since lot of new research and developments have been done. They are used in trucks, ships, submarines, locomotives, and in electric generating plants. Most of the modern heavy road vehicles, large scale portable power generators, and most farm and mining vehicles have diesel engines. Diesel engine continues to be most economical thermal engine till date. Even today diesel engine equipment is the first choice of any person looking at the difference in price and efficiency compared to gasoline. Lot of research work is going on to improve the efficiency and reduce the pollutants. The new diesel engine designs have advanced computer control that eliminates many of these disadvantages like noise, smoke, vibration and high cost. In the coming years, we are likely to see many more diesel engines vehicles on the road.













